Describe How Bone Cells Are Organized in Bone Tissue
The matrix for bone is laid down in thin layers called lamellae. There are three types of cells that contribute to bone homeostasis.

Classification Of Bone Tissue Cells Osteogenic Cells Osteocytes Download Scientific Diagram
The lamellae are arranged in concentric patterns around tubescalled osteonic canals.

. Compact bone consists of closely packed osteons or haversian systems. Describe how bone cells are organized in bone tissue Bony matrix is deposited by OSTEOBLASTS in a thin layer called LAMELLAE which form circular patterns around capillaries within longitudinal tubes called central or HAVERSIAN CANALS. According to a new.
This type of blood cell is within the bone. - Osteogenic cells cell division turn into osteoblasts - Osteoblasts bone building synthesize ECM - Osteocytes mature bone cells exchange nutrients and wastes with blood. This is a very large cell formed in bone marrow.
These bone cells have distinct features structure and considered essential functions. This type of cell is within the bone. Four types of cells are found within bone tissue.
Bone lining cells are quiescent flat-shaped osteoblasts that cover the bone surfaces where neither bone resorption nor bone formation occurs. Adipose cells or adipocytes are specialized cells that store fat and synthesize hormones growth factors and some inflammatory mediators. Bones are essentially living cells embedded in a mineral-based organic matrix.
As the secreted matrix surrounding the osteoblast calcifies the osteoblast become trapped within it. When adipocytes are clustered in large numbers they are referred. - the types of cells present and their function - what is the matrix made of - the function of compact and spongy bone - the organization of the matrix for compact spongy bone Give at least 3 important characteristics of each that are.
27 2018 Bone marrow the spongy tissue inside most of our bones produces red blood cells as well as immune cells that help fight off infections and heal injuries. Bone tissue is made up of four different types of bone cells. Osteoblasts are bone-forming cell osteoclasts resorb or break down bone and osteocytes are mature bone cells.
Although bone cells compose a small amount of the bone volume they are crucial to the function of bones. It helps to maintain bone as living tissue. There are three types of bone cells present in human body.
The endosteum contains osteoprogenitor cells but does not appear to contain either. Is the bone cell responsible for forming new bone and is found in the growing portions of bone. Both the compact and spongy bone tissues are composed of 3 main types of bone cells.
This extracellular matrix is made of. The bone cells coordinated actions determine the shape and form of body. Osteoblasts osteocytes osteoclasts and osteoprogenitor cells.
Bone tissue is a specialized connective tissue composed of organic and inorganic fractions. The organic fraction consists of specialized bone cells including osteoclasts osteoblasts and osteocytes and of an extracellular matrix mainly composed of type I collagen osteopontin osteocalcin and proteoglycans. Its cytoplasm extends along the bone surface and displays few cytoplasmic organelles such as profiles of rough endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus 50 Figure.
Its function is to form new bone tissue. Osteoclasts develop from monocytes and macrophages and differ in appearance from other bone cells. These bone cells are Osteoclasts Osteoblasts and Osteocytes.
Osteoblasts osteocytes osteogenic cells and osteoclasts Figure 5. As a result it changes in structure and becomes an osteocyte the primary cell of mature bone and the most common type of bone cell. However in different locations in bones these cell types have different functions.
Bone Cell 1. Its function is to absorb and remove unwanted tissue. This post is used to express the cell types in bones.
Cartilage adipose tissue bone and blood are specialized connective tissues. Osteogenic cells are undifferentiated and develop into osteoblasts. Describe 4 types of cells present in bone tissue.
Compact and Spongy bones Describe the basic structure of each type of bone including. Between the layers of lamellae theosteocytes. Together these cells comprise the compact and spongy bone layers and work together to maintain the mineral composition and structure of the bones.
Description Describe bone tissue. This cell is strongly basophilic and cuboidal or pyramidal in shape and its nucleus is large with a. These bone cells are embedded in the matrix of bony tissue and perform many vital functions.
There are four types of cells in boneosteocytes osteoclasts osteoblasts and osteoprogenitor cells. Osteocytes maintain the mineral. Each osteocyte is located in a small cavity in the bone tissue called a lacuna lacunae for plural.
An equilibrium between osteoblasts and osteoclasts maintains bone tissue. The goal of these strategies is to exploit the bodys natural abil- Bone tissue is composed of bone matrix and bone cells. They are located in loose connective tissue either as individual cells or in clusters.
Bone or osseous tissue is a hard dense connective tissue that forms most of the adult skeleton the support structure of the bodyIn the areas of the skeleton where bones move for example the ribcage and joints cartilage a semi-rigid form of connective tissue provides flexibility and smooth surfaces for movementThe skeletal system is the body system composed of bones. This is concerned with bone formation and is found in the growing surface where the bony matrix is deposited. These cells exhibit a thin and flat nuclear profile.
The endocortical surface of a bone faces the medullary canal and is lined by the endosteum a single thin layer of bone lining cells mature osteoblasts and osteoblasts which form a membrane over endocortical and trabecular bone surfaces to enclose the bone marrow Figure 2G. The different types of bone cells include. When osteoblasts get trapped within the calcified matrix their structure and function changes and they become osteocytes.
Osteogenic cells are hanging around waiting to deal with traumas or problems with the bone where they will have to produce new bone. Organic components being mostly type 1 collagen. Four types of cells are found within bone tissue.
Bone ity to repair injured bone with new bone cells and to remodel the matrix is primarily built of type I collagen 90 with the remain- new bone tissue in response to local stress factors. There are four types of bone cells in bone tissue. Bone tissue is continuously remodeled through the concerted actions of bone cells which include bone resorption by osteoclasts and bone formation by osteoblasts whereas osteocytes act as mechanosensors and orchestrators of the bone remodeling process.

Hierarchical Organization Of Bone Tissue A Macrostructure Of Download Scientific Diagram

Bone Lining Cell An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Bone Bone Morphology Britannica

Ijms Free Full Text Strategies For Bone Regeneration From Graft To Tissue Engineering Html

Pin On For Human Anatomy Physiology

6 3 Bone Structure Anatomy Physiology

Included Is A Two Page Reading Passage Covering The Different Levels Of Organization Including Reading Lessons Levels Of Organization Biology Biology Worksheet

Classification Of Bone Tissue Cells Osteogenic Cells Osteocytes Download Scientific Diagram
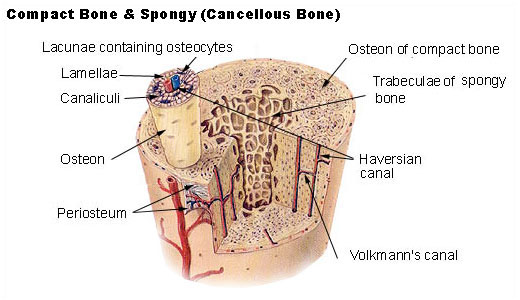
Seer Training Structure Of Bone Tissue
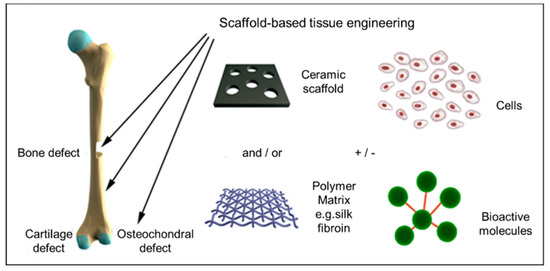
Bioengineering Free Full Text Mineralization Of Biomaterials For Bone Tissue Engineering Html
![]()
Animal Tissues Bone Atlas Of Plant And Animal Histology
![]()
Animal Tissues Bone Atlas Of Plant And Animal Histology

Hierarchical Organization Of Bone Tissue A Macrostructure Of Download Scientific Diagram

Types Of Human Cell Nerve Cells The Cells That Make Up The Nervous System And The Brain Are Nerve Cells Or Neurons Electri Types Of Humans Nerve Cell Cell

6 Bone Pocket Dentistry Loose Connective Tissue Anatomy And Physiology Human Anatomy And Physiology
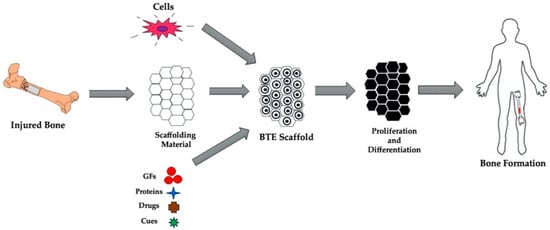
Jfb Free Full Text Conductive Scaffolds For Bone Tissue Engineering Current State And Future Outlook Html

Tissues And Other Levels Of Organization Organization Tissue Levels

Body Organization Activity Human Body Reading Reading Comprehension Worksheets Differentiated Reading Passages

Comments
Post a Comment